Business flow automation software using bots or AI to optimize efficiency, scalability, quality, and consistency in processes and decisions.
What is Automation?
A century ago, post industrial revolution, automation was leveraging wheels, gears and motors to ease of daily living in areas such as, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation.
More recently with the information age revolutionizing communication, record keeping, and other facets of our work, many ERP systems were developed. They helped manage business and functional processes and procedures of organizations and industries, enabling the companies to grow at even a faster pace. To highlight some of the ways that automation played a significant role in companies:
-
Enhance productivity
-
Reduce redundancies and waste
-
Streamline and track processes
-
Faster time to market and/or enabled just-in-time to market
-
Minimize human errors and improve output quality and consistency
-
Provide scalability
What is Robotic Process Automation(RPA) for?
In the current era of digital transformation, most businesses depend on IT enabled processes. With a significant advantage in time to market, many functional areas of corporations choose their technology or solution based on a cost benefit analysis specific to their project/product, potentially resulting in implementing more and more variety of technologies and solutions with each completed project at the company.
In many cases, organizations decide that the immediate benefits and enablements offered by this approach outweighs the need for more consolidated and holistic planning and solutioning strategy which can:
-
Provoke conflicts between functional areas that need to be settled,
-
Require impactful changes and/or a shift in resources throughout the enterprise, and thus,
-
Significantly slowing down (if not, halt) the successful completion and implementation of the solution.
However over time, the continued implementation and operations of these siloed products can hinder and detract the company’s ability to continue scaling and evolving with the market. For example, a loan required know-your-customer (KYC) product from one vendor may not be able to effectively trigger loan disbursement on a core banking product from different vendor. Such technical gaps would need to be bridged through, either, manual interventions that slows down the loan approval and disbursement cycles, or another technical integration project/solution for the two specific systems; costing the organization more time, effort, technology, and money.
Enter RPA technologies and solutions. For organizations that find themselves in the above or similar situations, RPA can enable integrations across multiple software product silos and automate various actions, transactions, and processes to provide the cross-systems interoperability.
Where and how can RPA be leveraged?
Per Gartner’s research, RPA software market remains the fastest-growing enterprise software segment, at a rate of 38.9% in 2020.(1) The five common use cases for RPA being:
-
Automate via user interface (UI) integration – Leverage the user interface to perform tasks and automate unattended processes between applications where no back-end integration or API is available.
-
Augment knowledge workers – Saving effort of knowledge workers and enhancing their ability to get work done even faster.
-
Accelerate citizen automation – Citizen developers (employees without coding skills) build automation scripts using low/no-code interfaces, guided navigation, drag and drop workflows, configurations, etc.
-
Automate document processing – Allowing organizations to automatically adjust, sort, label, and process physical documents by extracting and saving text and other contents from them.
-
Create headless bots – Workflow components can run on schedule or trigger basis, interacting with APIs to get the work done; usually consumed by orchestration engines, bots or applications.
Looking at industry level use cases:
-
Insurance – enrollment and eligibility, prioritizing and assigning claims, claims processing and administration, report automation, etc.
-
Financial – regulatory compliance, new application processing, credit decisioning, mortgage and loan KYC, etc.
-
Healthcare – medical record keeping and data management, operational analytics, patient pre-authorization, medication and prescription management, claims processing, etc.
-
Manufacturing – invoice verification, receipt confirmation, freight costing, logistics and distribution, purchase order processing, etc.
RPA can also be applied to a variety of other and more general business areas and functions to gain benefits – ROI, productivity, cost savings, accuracy and quality, and personalized customer experiences.
What are the leading products?
There are numerous products in market already. From Gartner’s magic quadrant for RPA(1) – UiPath, Automation Anywhere and Blue Prism have been maintaining their positions in the leader quadrant for the past three years. Workfusion is another product which was able to get itself into leader quadrant in 2020, but was pulled down to visionaries in 2021. Microsoft’s Power Automate is another product which has gained a lot of momentum in the last two years and reached leader quadrant. Power Automate has its edge over other offerings in that it can provide seamless integrations with other Microsoft products and Azure cloud with its simplified billing options.
How to choose the right product?
To choose the right product for automation, maturity of products needs to be evaluated against the use cases where it needs to be applied. Based on Gartner’s market research following were the products leading in each area.
.png?width=750&height=532&name=image%20(38).png)
Note: The matrix mainly focuses on broad spectrum RPA products that can benefit larger and more mature companies with multiple use cases to consider for implementation.
For a given organization, there may be one or more use cases to consider when searching for the fit within these product/service offerings. Looking at the forest, instead of the individual trees, so to speak, may afford the company with the proper set of information to define the right solution that will hold resilient in the future.
Hyperautomation
Once the right tools are chosen, various silos can be connected together. Measuring effectiveness in such automation, collecting statistics, ROI evaluation and continuous improvement of business processes based on data is the logical next step. Data from various sources analyzed through machine learning models can drive intelligent automation or hyperautomation.
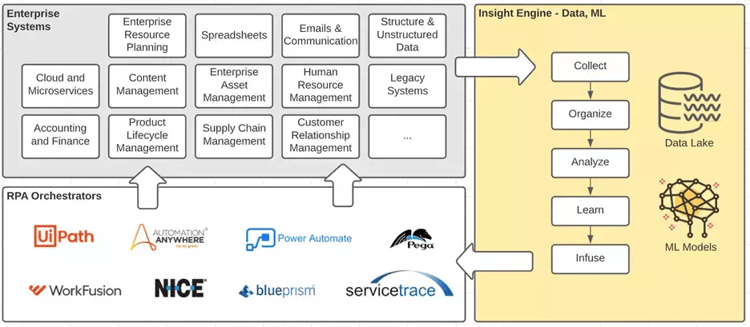
Hyperautomation requires a well-orchestrated collection of technologies, tools, and solutions, including:
-
AI/ML
-
RPA
-
low-code/no-code tools
-
transactions and events driven architecture
-
business and data integration, process, and decision management solutions and platforms
Dimiour is a digital transformation partner specializing in and equipped with the right set of frameworks and the expertise to take enterprises on their hyperautomation journey.
References
- Gartner – https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-27LG7KS8&ct=211005&st=sb
- UiPath – https://www.uipath.com/product
- Automation Anywhere – https://www.automationanywhere.com/rpa/robotic-process-automation
- Blue Prism – https://www.blueprism.com/
- Microsoft Power Automate (Formerly Microsoft Flow) - https://powerautomate.microsoft.com/en-us/robotic-process-automation/
- Pegasystems – https://www.pega.com/products/platform
- WorkFusion – https://www.workfusion.com/platform/
- NICE - https://www.nice.com/rpa/
- Servicetrace – https://www.servicetrace.com/products/xceleratorone-x1-rpa/

